Product management is a multifaceted discipline where you don’t get the chance to get bored. In this article, we’ll take a look at product management from a different angle — that of risk management.
We will look at the four big product risk dimensions defined by Marty Cagan and how effective risk management can help a product manager identify opportunities, test them, and drive value through successful products. We’ll also discuss a risk management framework to follow in your product management role.
Table of contents
- So what is a risk?
- What about product risks?
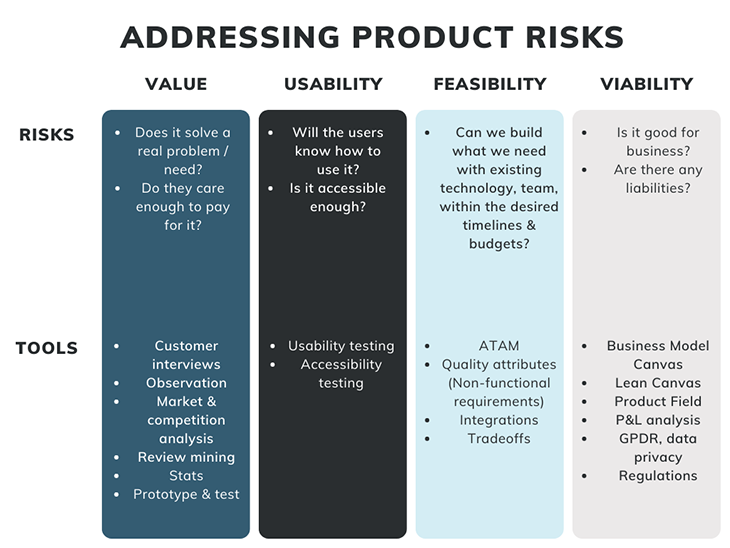
- Value risk
- Usability risk
- Feasibility risk
- Viability risk
- Risk management framework
So what is a risk?
According to the ISO-31000 standard on risk management, a risk is described as the “effect of uncertainty on objectives.” The definition has been simplified and adapted to the high-paced, uncertain times we are living in.
It focuses mainly on what effects incomplete knowledge of context, events, or situations may have on decision-making inside an organization. Risks may refer to both threats for an organization, but also opportunities.
What about product risks?
While the generic term of risk applies to an organization, product risk refers to the effect of uncertainty on developing a product. Compared to the more traditional approach of project or delivery management, where risks are mostly considered through the tactical lens of cost, time, team, quality, etc, we want to look at the more strategic aspects when referring to product risks.
As Marty Cagan nicely depicts it in his article Four Big Risks, product management is essentially about tackling four types of risk:
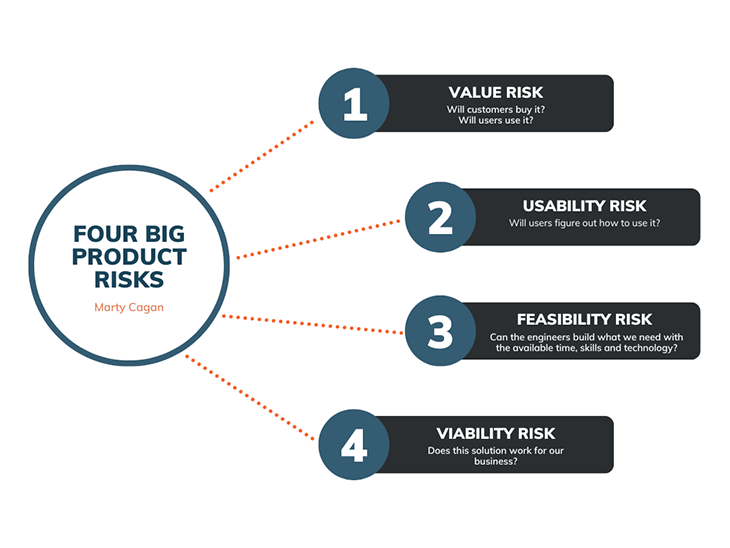
Compared to the well-known product management Venn diagram that describes a successful product at the intersection between the user, business, and technical, the model proposed by Cagan adds the fourth dimension to the mix: value.
Value risk
9 out of 10 startups will fail, and one of the main reasons is failure to find the product-market fit. The highest failure rate by industry is in information technology, followed by transportation and utility, retail, construction, and manufacturing.
So why does that happen?
- The company failed to identify a real problem/need in the market
- The identified problem/need was not painful enough for users/customers to pay for it
This, however, should come as no surprise to anyone working in product. It’s one of our tenets, after all — to always start from a problem/need and test/validate it before developing a new product no one will want or buy.
Below, you can find a list of tools in the PM toolbox that may come in handy when performing value risk management.
Identify opportunities worth addressing
Identifying opportunities worth addressing is one of the most critical aspects of product development and finding product market fit. You need to get out of the house, find your users (and don’t go talking with friends and family), go where they are, observe them, talk to them, and see what problems or needs they have. Then talk to some more people to see if what you identified applies to more than a handful of users.
Here are a couple of ways to get out to the field and really identify these opportunities:
- Customer interviews
- Observation
- Market and competition analysis (SWOT, Porter Five Forces, etc.)
- Review mining — check out competitor products and their reviews on various product directories to uncover hidden needs
- Stats, Reddit, or other online sources
Recommended resources:
Test buying intent
Once you have identified some opportunities on the market, you also want to see if people care enough about solving that particular problem or addressing that need to pay for it. For this situation, you should test early and often with minimum investment:
- Prioritize riskiest assumptions
- Prototype and test early and often
Recommended resources:
- Eric Ries, Lean Startup
- Type of MVPs
Usability risk
Now that you’ve established a market for the problem you are solving or the need you are addressing, you also want to ensure that the product you are building meets user needs and does not add extra frustration or friction.
Consider that 88 percent of online users will likely not return to a website after a bad experience, this may lead to customer loss or revenue. User experience (UX) plays a crucial role in addressing this risk.
An example of bad UX from the book Tragic design by Johnathan Shariat mainly stuck with me. It’s about the usability of medical software and how poor design contributed to a young girl losing her life.
Jenny was a cancer patient, and after a while, she needed to return to the hospital to undergo a strong chemo treatment. This treatment had some exceptional conditions under which it required to be administered. Namely, she was supposed to get three days of IV hydration pre-and post-treatment. The nurses treating her were all experienced practitioners, but due to various factors, they missed this critical information and did not administer the IV hydration to Jenny.
Shortly after, Jenny died. Of course, many factors were at play, and you could not blame her death on just one. But one cannot help but wonder if Jenny would have lived if the software had better signaled life-critical information about the treatment to the software operator. The black arrow on the screenshot shows the alert’s report and hierarchy in the whole screen’s context:
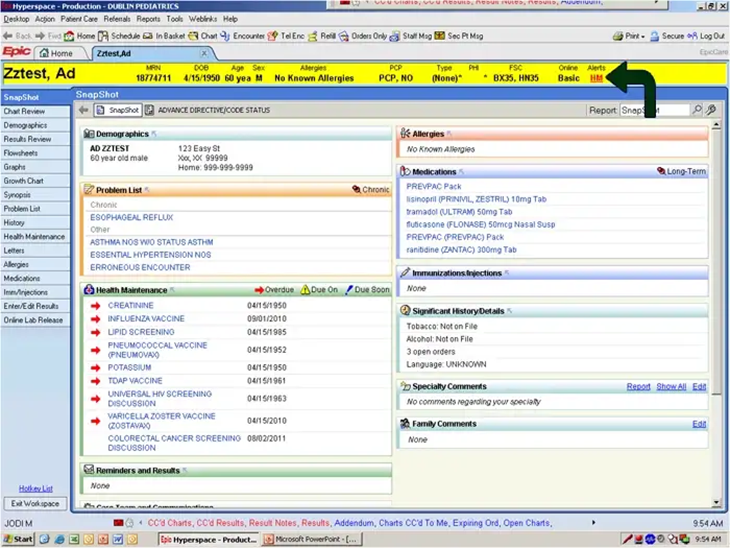
How do we ensure the experiences we design are suitable for our users and achieve their goals?
Usability testing your product
Usability tests help us answer such questions as:
- What usability issues do we have with our product?
- Can users accomplish the goals we aim our product for?
- What do the users really think of our system?
- What is the error rate?
Running regular usability tests helps you improve your product and uncover hidden opportunities along the way. The switch to hybrid and remote work has cleared the path for easier and faster ways to perform user testing.
Your best friends are the members of your UX team when it comes to performing usability tests, so make sure you keep them close and use their expertise.
Don’t forget about accessibility
While we discussed a lot about usability, one aspect that may get overlooked when designing digital products is accessibility. The topic is getting increased attention, and it is also an aspect you will want to test for, especially with the rising interest and the increased regulation around accessibility.
Here are a few ideas of how you could test accessibility on your own:
- Turn off your trackpad and use only the keyboard for navigation
- Turn off images
- Turn on high-contrast mode
- Check for captions or alt text for images
- Turn off CSS
- Check your contrast
- Use browser extensions to check your usability (here is a list to get you started)
Recommended resources
- Usability Testing 101 — NN Group
- Tragic Design — Johnathan Shariat
- How bad UX killed Jenny — Jonathan Shariat
- The worst UX failures
- User interview questions — Yale
- Designing for accessibility — Adobe
- The 6 Simplest Web Accessibility Tests Anyone Can Do — Karl Groves
Feasibility risk
This is the type of risk most people working with digital products for a long time are familiar with. It’s about technology, after all.
When tackling these risks, you want to address all aspects of technology and ensure you can deliver value to both business and users with the available technology, time, and skills. When tackling this kind of risk, your best friend is the architect/technical lead and your development team. This is where traditional project management can apply risk management frameworks.
Here are a few questions to get the conversation with your technical team started:
- What quality attributes does our solution need to meet?
- Think here about security, performance, scalability, maintainability, etc.
- What tradeoffs do we need to do to meet specific timeframes/budgets?
- What is the system context which our solution needs to integrate with?
- What technologies are the best suited to adhere to the defined quality attributes?
- What strategy should we approach to avoid technical debt?
To address this risk, your architect may want to use different scoring mechanisms, such as ATAM, to help explain and link technical decisions to the broader picture of the product, thus achieving a holistic view.
Recommended resources:
Viability risk
Last but not least, you also want to address the viability of your solution. Unless you live in a perfect world with unlimited resources concerning money, time, development, marketing and sales capabilities, and perfect users who all want your product, you need to pay close attention to the business side.
You must partner with your stakeholders to get their perspectives and devise strategies to address this risk. Depending on where your product is on the product life cycle, the aspects you will cover may differ, but here is a list to get you started:
- Business strategy
- What business objectives do we want to meet?
- How do we build a sustainable business model?
- Financial aspects
- What does our P&L look like?
- What margins are we targeting?
- Product marketing, brand, and reputation
- What is our go-to-market plan?
- What is our product’s brand story?
- What activities do we need to perform to drive the product further?
- Legal and compliance
- What are our legal and compliance requirements?
- Are there any liabilities?
Tools that may help you in capturing this type of risk:
- Business model canvas/lean canvas
- Product Field
Risk management framework
So, irrespective of what type of risk management you are performing, we recommend you consciously and continuously apply the five steps of the risk management framework:
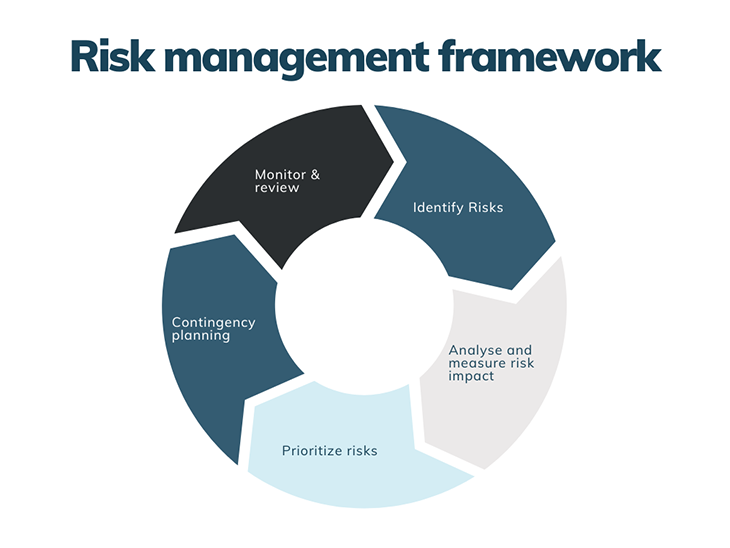
- Regularly identify new product risks — involve your team in this, as they may contribute with fresh perspectives
- Analyze and measure the risk impact — take some time to assess the likelihood and impact of each risk
- Prioritize risks based on the assessment performed in the previous step. You will be able to save a lot of time and help you focus on the most critical/urgent risks first
- Contingency planning — devise a strategy of how to tackle the prioritized risks
- Monitor and review — risk management is an ongoing exercise. It is not enough to perform this exercise once and forget about it. You need to constantly monitor and review your risks and adjust course if needed
Conclusion
Practicing continuous product risk management helps you in multiple ways. It helps build the habit of addressing risks and validating early and often, gives you intel and data you can use in product review meetings, and provides a communication tool to help align all relevant stakeholders around product management best practices.
Thanks for reading, I hope you found the article helpful!
Featured image source: IconScout
The post How to effectively manage product risks as a product manager appeared first on LogRocket Blog.
from LogRocket Blog https://ift.tt/83FAKhB
Gain $200 in a week
via Read more



