As a product manager or a product owner, you often need to make a decision on whether to enter into a new market with your product. Before jumping in, it is important to scope out the market to better understand your chances of success.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis is an excellent tool for exactly this purpose.
Table of contents
- What is Porter’s Five Forces analysis?
- History of Porter’s Five Forces model
- What are Porter’s Five Forces?
What is Porter’s Five Forces analysis?
Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a model that identifies and examines five competitive forces that affect every industry. The structure of an industry is typically identified using the Five Forces analysis to develop company strategy. Any sector of the economy can benefit from using Porter’s model to better analyze industry rivalry and increase long-term profitability.
History of Porter’s Five Forces model
Michael E. Porter’s 1980 book Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors contains the Five Forces model.
Porter believed that the traditional approach to creating a strategy — a formula for competition, goals, and policies to attain those goals — was outdated and required updating. Porter examined the strategic needs of industrial sectors as a whole rather than simply individual enterprises. He did this by applying microeconomic principles to company strategy.
What are Porter’s Five Forces?
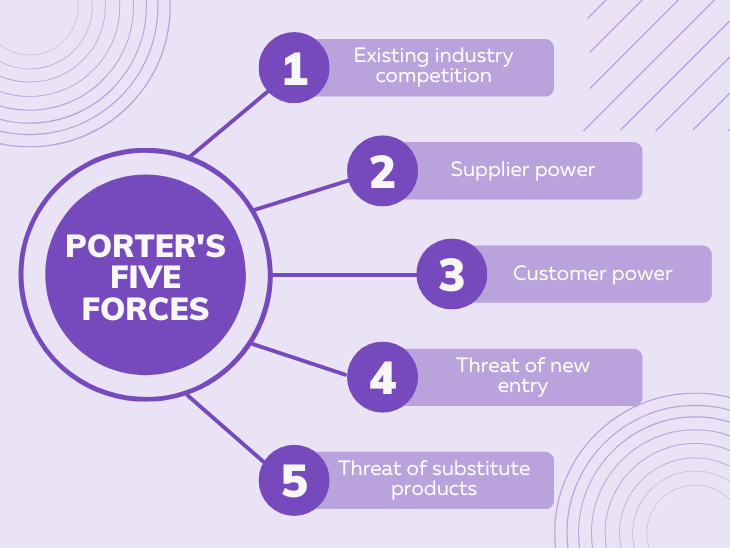
Porter’s Five Forces are:
- Existing industry competition
- Supplier power
- Customer power
- Threat of new entry
- Threat of substitute products
1. Existing industry competition
Existing industry competition is the first of the Five Forces. This measures the number of competitors and their ability to undercut a firm. The power of a corporation decreases as the number of competitors and the number of comparable goods and services they provide increases.
All variables aside, if a competitor can provide a better deal or lower rates, suppliers and customers will most likely favor them. On the other hand, when there is little competition, a corporation has more bargaining power and can raise or lower prices as they please.
2. Supplier power
The Porter model’s second element examines how quickly suppliers can raise input costs. It is influenced by the number of suppliers, the degree to which these inputs are special, and the cost to a corporation of switching providers.
The fewer suppliers in an industry, the higher the dependency a company has for them. As a result, the supplier is in a stronger position and has more flexibility with input costs and trade benefits.
The opposite is also true. If there are more suppliers in an industry, the company tends to have more bargaining power with input costs.
3. Customer power
Porter’s third force considers the market intensity. It is influenced by the quantity of consumers in the market and the products available in that market.
When a market is concentrated but products are undifferentiated, the buyer has greater bargaining power in price, quality, and services. You want to make sure your customers have low bargaining power to ensure your profit is at its highest.
Consider Apple: it has high switching costs for their consumers. They created the “Apple ecosystem” that allows for all their products to be interconnected and synchronized to provide the best user experience as possible. Not only does switching brands cost the consumer money, but also time and convenience.
4. Threat of new entry
The threat of new entrants into a market has an impact on a company’s power as well. An established company’s position may be considerably undermined the quicker and cheaper it is for a rival to enter and overtake its market.
The stronger the entry barriers, the greater the chance for companies to charge higher rates and negotiate better conditions.
5. Threat of substitute products
The fifth and final force focuses on alternatives. The presence of a substitute product threatens the sale of a company’s product. The more substitutes there are in a market, the less price flexibility a company has. A market with multiple alternatives forces a company to follow or mirror the price points of their competitors.
Advantages of using Porter’s Five Forces
The advantages of Porter’s Five Forces are as follows:
- Estimate the industry’s level of competition
- Display the areas where the threats and strengths are
- Determine which groups possess the power
- Highlight potential business growth opportunities
- Understand corporate risk
- Maximize corporate strategy
Estimate the industry’s level of competition
Porter’s Five Forces provides a way to quantify the threat of substitutes, the threat of new competitors, and the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers. These factors taken together will estimate the industry’s competition intensity. This will help the business comprehend the industry’s present competition and modify its corporate strategy accordingly.
Display the areas where the threats and strengths are
A company can identify its threats and strengths through understanding the buyer/supplier force, the risk of new competitors, and the alternatives in the market. The administration will be able to take preventative measures for the impending threats and determine the exact sectors where the company’s strengths lie.
Determine which groups possess the power
Porter’s Five Forces are linked to three different groups: suppliers, consumers, and rivals. Identifying which groups have more power helps the business choose the most effective handling method.
Highlight potential business growth opportunities
The industry’s power of suppliers and buyers will assist the business in deciding how, if, or when to vertically integrate. According to the information provided by the Five Forces, the firm may easily do one of two things: carry out forward integration to acquire their customer side of the value chain or carry out backward integration to buy their supplier side of the value chain.
To lessen the risk of competition, the company can consider the idea of undertaking horizontal integration to acquire a rival in the market. This will help the company get insights into the competitive rivalry.
Understand corporate risk
On a high level, corporate risk is the liabilities and threats that a firm encounters. The power of suppliers, consumers, and competitors can all be better understood by considering Porter’s Five Forces.
The corporation will be able to further understand its risks and respond to them more accurately. Companies will be able to prevent losses by placing more emphasis on spotting risks and controlling them before it’s too late.
Companies will then act more confidently when making business decisions if they can control risk.
Maximize corporate strategy
A corporate strategy will try to determine a company’s total worth, define strategic objectives, and inspire staff to meet those objectives. It is an ongoing process that needs to be carefully customized to react adequately to shifting market conditions.
Taking the impact of external forces into account, Porter’s Five Forces offers useful information to create or improve corporate strategy which maximizes value.
How to conduct a Five Forces analysis
To demonstrate how the model works in practice, let’s walk through an example Five Forces analysis for American Airlines.
Existing industry competition
We can analyze the U.S airline industry’s existing competition through many variables. First, many low-cost carriers have entered the market. Low-cost airlines such as Spirit, Allegiant, and Frontier create high competition in the market catering towards price-sensitive consumers.
There are also very strict industry regulations. Not only does this regulate safety, but it creates high fixed costs that make it extremely difficult for businesses to exit the market. This results in a stagnated industry; the businesses who are in the market stay in but rarely leave.
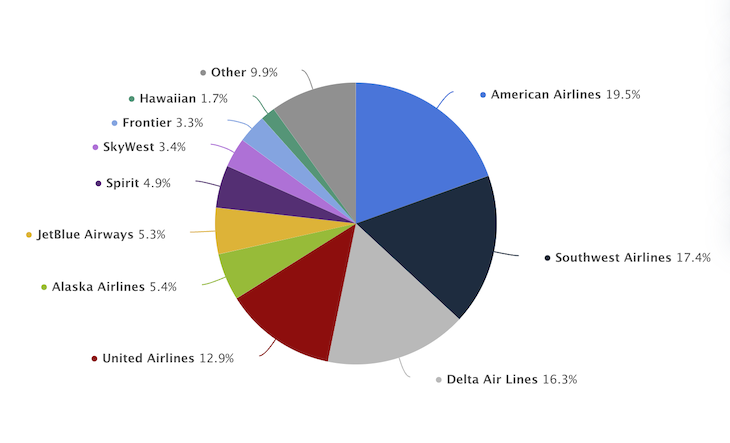
The switching costs for consumers are also low. Unless consumers have credit cards or flying miles with an airline, it is easy to switch to another for whatever reason. The fact that many industry participants are of a similar size (see graph below) intensifies the competition. When seen as a whole, the airline industry’s current rivals are very competitive.
Supplier power
The airline industry’s suppliers have a very strong negotiating power. The two main inputs that airline firms require are fuel and aircrafts. However, the external environment — which the airline firms themselves have limited influence over—has a significant impact on these inputs.
Oil is a limited resource that is vulnerable to significant swings in price due to geopolitical factors. We saw this post-pandemic when the price of flights skyrocketed because fuel was so expensive.
The type of aircraft is also something airlines have little negotiating power over. For instance, there are only two major aircraft providers: Boeing and Airbus. This means that they have major control over pricing and other variables.
Customer power
Customers have significant negotiating power in the airline industry. The prices of various airlines are available for comparison at the click of a button. Because of the low switching costs and the convenience of price comparisons, customers are more likely to fly with the cheapest airline.
In an attempt to reduce this, airlines offer credit cards, frequent flier miles, and rewards to increase switching costs and create stronger brand loyalty. Despite this, brand loyalty is not as strong as price sensitivity in the airline industry.
Threat of new entry
It is safe to say that the threat posed by new competitors in the aviation sector is low to medium. To launch an airline firm, you have to invest significantly upfront (e.g., purchasing aircrafts). Additionally, it can be difficult to acquire the licenses, insurance, distribution networks, and other qualifications that newcomers require (e.g., access to flight routes).
It is reasonable to assume that current players have amassed a sizable amount of experience over the years to reduce expenses and improve service standards. A newcomer will probably lack this kind of knowledge, which will put them at a competitive disadvantage from the outset.
Threat of substitute products
The airline industry generally fulfills the need for travel. There are many alternatives that you can take for travel instead of flying. You can decide to travel via train, bus or car, depending on the distance and urgency.
In Asia, bullet trains and Maglev trains are becoming increasingly popular. Elon Musk also proposed the Hyperloop, a form of travel in which passengers would travel in capsules in a vacuum tube at speeds up to 1200 km/h. Both of these could pose a severe threat to the airline sector in the future.
The threat of substitutes in the airline business might be rated as at least medium to high when all of this is considered.
Porter’s Five Forces vs. SWOT analysis
Porter’s Five Forces and SWOT are essentially two different approaches to address the same fundamental questions:
- How is a company currently positioned?
- What are its prospects for the future?
These are helpful on a personal level, but they’re also significant inquiries for possible investors. It is necessary that they grasp this type of analysis. Choosing an investment strategy is partially a question of personal preference, but it also depends on how developed a firm is and how developed its respective sector is.
The Five Forces approach is typically more helpful and instructive for young businesses and emerging industries, whereas SWOT provides more insight into the present and future of more mature businesses.
Porter’s Five Forces analysis template
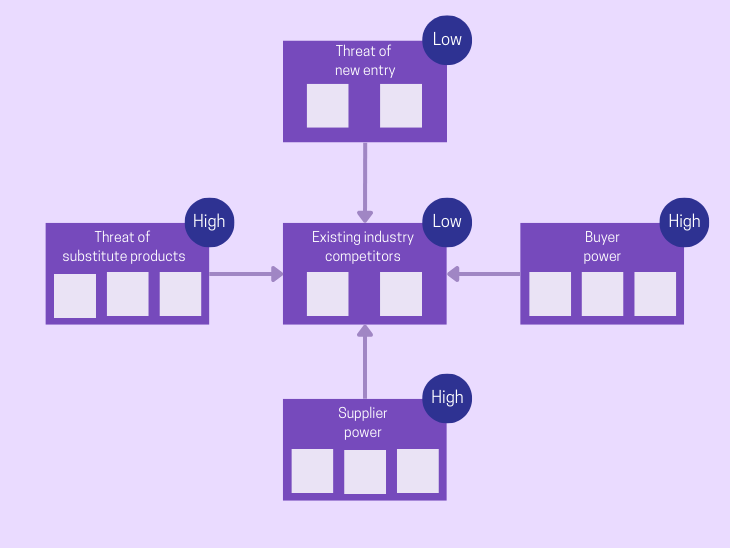
The Five Forces template allows you to succinctly describe and collect all the relevant information required to conduct the Five Forces analysis. Each gray box can denote an entity and each section can have any number of gray boxes depending on the market. The template can also be used to highlight which of the five forces should have the highest priority for the business.
Conclusion
When examining a corporation’s competitive environment, the most crucial factors to be taken into account are included in Porter’s Five Forces model.
High threat levels often indicate a potential revenue loss in the future, and vice versa. For example, if entry barriers are absent, a young business in a rapidly expanding field may find itself shut out very quickly. Similarly, a corporation providing products with many alternatives might not be able to use pricing power to increase margins and may even lose market share to rivals.
Businesses use Porter’s approach because it compels them to consider their whole sector when developing long-term strategies, instead of short-term business plans. Porter’s Five Forces model still is a vital tool utilized to develop a corporate plan.
The post What is Porter’s Five Forces analysis? appeared first on LogRocket Blog.
from LogRocket Blog https://ift.tt/XS4EtfC
Gain $200 in a week
via Read more



