The most common reason that a product fails is because the focus is on the technology that is used in the product and not the problem that it is solving.
To avoid falling into this trap, you need to make sure that you are clear on the scope and the practical application of the product. Once you understand what to do and how to do it, the rest of the process becomes easier.
The product canvas helps you do precisely that.
Table of contents
What is a product canvas?
A product canvas is a framework designed to construct products and generate feature developments. It follows lean and agile methodology’s principles. Its primary purpose is to present a complete view of the product in a single document that can be then used to create a product roadmap.
The product canvas mainly has nine blocks and each block focuses on a specific part of the planning and development of the product. When put together, the product canvas provides a 360-degree view of the vision and scope of the product.
What is the product canvas used for?
Using a product canvas is a great way to ensure that the technical teams and the business teams are on the same page about the product and that there is a common understanding of what you are trying to build.
With a product canvas, teams can map out the start-to-end lifecycle of a product, which would commonly include things like the problem, the solution, the target customers, and the KPIs to measure success all in a single view.
Often, teams fail to focus on the business goal of the product by overdoing it on the development side, resulting in the downfall of the product. A product canvas can help teams identify the strategic value that their product adds and the performance metrics that measures impact that it creates. This is crucial because failure to understand these will probably lead to issues in the product development cycle.
Below is an example of what a product canvas looks like for CloudFire (a media sharing platform for parents):
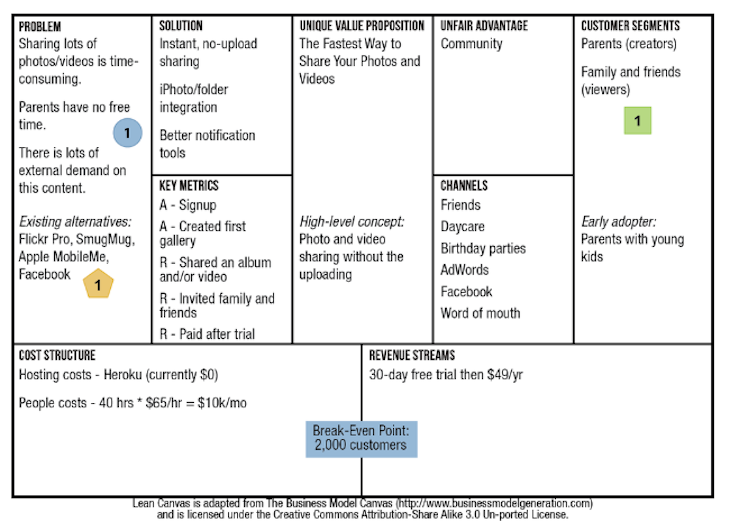
How to build a product canvas
Building a product canvas involves the following steps and considerations:
- Begin with the problem
- Think about the solution
- What is unique about your solution?
- What are your customer segments?
- What are your channels to reach customers?
- Cost structure
- Revenue streams
- Key metrics to measure success
- What is your unfair advantage?
1. Begin with the problem
As a product manager, one of your key tasks is to guide product discovery to uncover the most vital part of the product – the problem it solves. If this is not done properly, there is a very good chance that you will end up creating a solution to a wrong problem or, even worse, creating a solution to a problem that never existed.
Having a clear, well-defined problem prevents the team from deviating and enables it to pinpoint a clear solution.
A good way to fill the “Problem” block is to ask a few key questions:
- What is the problem you are trying to solve?
- Why is it a problem?
- Who faces the problem?
- What are the existing alternatives to deal with the problem?
It is very surprising to see how these four questions can clear so many things about the problem. While these are a great starting point, there is more that comes after. The responses from the user clarify which questions to ask next. Make sure you record the answers given by the interviewees and clearly highlight what each answer signifies.
2. Think about the solution
When thinking about the solution, the most effective way to fill this block on the canvas is to think about the simplest way in which you can solve the problem.
It is easy to fall into the trap of focusing on fancy terminologies and methods, such as deep learning, neural networks, big data, AI, etc., but remember the principle of lean methodology: “Test fast, fail fast and adjust fast.” So start with the most objective solution and build on it.
Key questions to ask here are:
- What kind of solution are we going to build?
- What do we expect the solution to do?
- What are the inputs and outputs to our solution?
3. What is unique about your solution?
When filling this block, think about the differentiating factor that makes your solution better than the solutions already present in the market. This could be the way your solution is built, the algorithm behind the solution, the output format of the solution, etc.
Key questions to ask here are:
- Why would customers buy our product over others?
- Is our solution faster/ safer/ more efficient/ more secure/ more convenient?
- Does it help customers save anything? (time, money, effort, etc.)
4. What are your customer segments?
It is possible that the solution you are building is used by two different kinds of customers with two completely different applications. It is important to identify these different customer segments and decide which segment the product is for.
Focusing on a single customer segmentation allows for the problem to be more clearly identified. Also, it is important to decide who your early adopter is so that you can market the product accordingly in the early stages.
A marketplace-like platform is a great example of a product having two customer segments: a buyer and a seller. Both use the same product but for two completely different purposes.
5. What are your channels to reach customers?
For any product to be successful, it needs to be used by the customer. To get the product into the hands of the customer, you have to decide the path to reach them.
While the initial goal of any product is to learn and not scale, it is helpful to have a plan to get the product in front of users. Depending on the resources available, communication channels to customers can either be free with word of mouth or paid with Google Adwords.
6. Cost structure
When starting out with the development of a product, it is beneficial to have an understanding of the costs you will incur. This does not have to be super detailed and accurate, but a ballpark figure of the costs will help you plan out the budget and allocate your resources accordingly.
Costs could include server costs, data storage costs, people resources costs, etc. Some key questions that can help are:
- What will it cost to build the initial MVP?
- What are our variable and fixed costs?
- What is our ongoing burn rate?
- What is the burn rate for the first 12 months?
7. Revenue streams
When you have a new product or service, customer acquisition is most likely the goal. Eventually you will have to figure out how you are going to make money off the product, and who the paying customers will be.
It’s important to note that not all users will pay, meaning that not all users will be the customers. Also, you don’t need a lot of users to support the growth of a product in its early stages – just a few good customers will do just fine!
8. Key metrics to measure success
According to Norm Brodsky and Bo Burlingham, authors of The Knack, the definition of key metrics to measure success is “the key number that tells you how your business is doing in real time, before you get your sales report.”
Every product or business has a few key numbers that can help them gauge whether their product is doing well and customers like it. These numbers are crucial in determining product progress and identifying key parts in the customer lifecycle.
Some of the most common metrics are customer acquisition rate and cost, customer retention rate, revenue, profit, customer activation points, and referral rate.
The idea of the key metrics is essentially to answer the following important questions:
- How are users finding you?
- Are they having a good first experience?
- Are they coming back after using the product for the first time?
- What are avenues to make money?
- Who are your customers or customer segments that are paying you?
- Do users tell other potential users about your product or service?
9. What is your unfair advantage?
This is usually the most difficult block to fill. The most common mistake to make while filling out this block is to confuse advantage with the features of the product.
Unfair advantage is an edge that you get which cannot be easily copied or replicated by other products or competitors. Some examples of unfair advantage are:
- Your dream team
- Global events
- SEO ranking
- Community
- Personal authority
- Patented aspects of the product
It is okay to leave this part of the product canvas blank when you start out initially but the idea of this block is to make you, as a product manager, think about your differences and how to make them count.
The post The product canvas: How to build one in 9 steps (with examples) appeared first on LogRocket Blog.
from LogRocket Blog https://ift.tt/E1xgXZN
Gain $200 in a week
via Read more



