The Graph is an indexing protocol for organizing blockchain data. It uses a GraphQL API to provide easier access to on-chain information than the traditional method of sending an RPC call.
The network organizes the data with subgraphs; open-source APIs that are created by the community and are used for retrieving data from Indexers, Curators, and Delegators.
In this article, we’re going to be taking a look at how you can use The Graph and subgraphs for Web3 data querying.
- Indexers operate the network nodes
- The Graph Foundation
- Create project on Hosted Service
- Deploy subgraph
Indexers operate the network nodes
Indexers operate the nodes of the network, which index data and serve the queries.
Since the Graph Network uses a proof-of-stake algorithm, indexers stake Graph Tokens (GRT) to provide indexing and query processing services. In turn, Indexers can earn query fees and indexing rewards.
They select subgraphs to index based on the subgraph’s curation signal. Applications that consume the indexers data can set parameters for which Indexers they want processing their queries, along with their preferences for query fee pricing.
Curators signal high quality subgraphs
Curators organize data from the subgraphs by signaling on the subgraphs that should be indexed by the Graph Network.
They do this using Graph Curation Shares (GCS), which allow them to place the equivalent of an investment on a subgraph.
Curators stake GRT, which allows them to mint GCS. Each subgraph has a bonding curve that determines the relationship between the price of GRT and the number of shares that can be minted.
According to the Graph’s documentation, curating is considered risky and should only be performed after thoroughly researching and investigating the trade-offs involved.
Delegators secure the network by staking
Delegators stake GRT to one or more Indexers to help secure the network without having to run a node themselves.
Delegators earn portions of the Indexer’s query fees and rewards, which is dependent on the Indexer’s and Delegator’s stake, along with the price the Indexer charges for each query.
Allocating more stake to an Indexer allows more potential queries to be processed. The Graph’s documentation claims that being a Delegator carries less risk than being a Curator because they are not exposed to fluctuations in the price of GRT, due to burning shares of GCS.
The Graph Foundation
The Graph is developed and maintained by The Graph Foundation. To make sure the network and larger community continues to improve, the foundation distributes grants (called Graph Grants) to community members working on protocol infrastructure, tooling, dApps, subgraphs, and community building.
Three different graph services
There are three different ways to interact with the Graph if you are not hosting your own subgraph:
- Graph Explorer: Explore different subgraphs and interact with the Graph protocol
- Subgraph Studio: Create, manage, and publish subgraphs and API keys using Ethereum Mainnet
- Hosted Service: Create, manage, and publish subgraphs and API keys using other networks aside from Ethereum, such as Avalanche, Harmony, Fantom, and Celo
The hosted service does not require a crypto wallet and can be used with a GitHub account. The Graph Explorer and Subgraph Studio will both ask you to connect a wallet such as MetaMask or Coinbase.
Create project on Hosted Service
After creating an account on the hosted service, click My Dashboard on the navigation bar to see your dashboard.
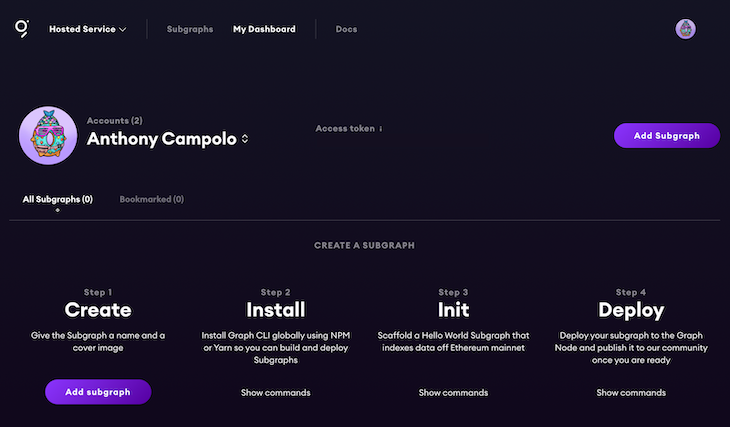
Click Add Subgraph to create a subgraph.
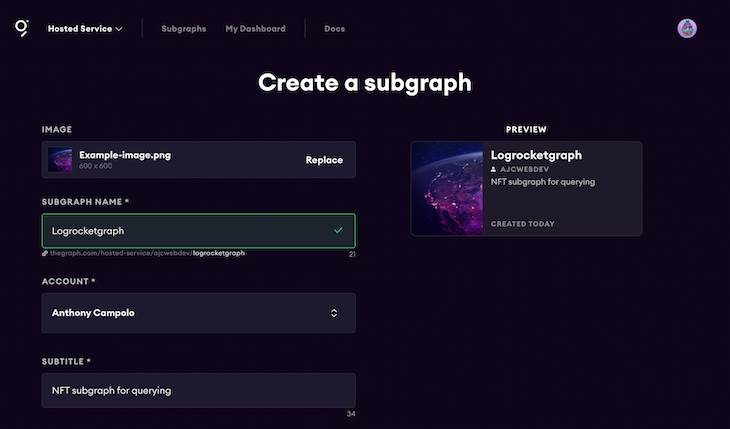
Add a name and subtitle for your subgraph. Once you’ve filled in your subgraph’s information, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Create subgraph.
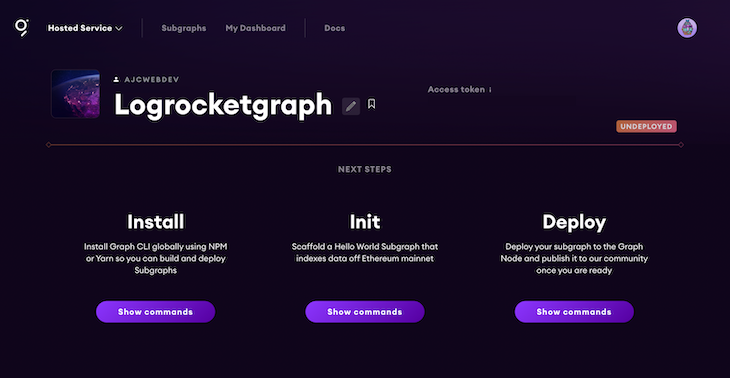
With our subgraph setup on the hosted service, we can create our project files. Create a new directory, initialize a package.json, and install dependencies.
mkdir graphrocket cd graphrocket yarn init -y yarn add -D @graphprotocol/graph-cli @graphprotocol/graph-ts
Copy the access token available on your project dashboard on Hosted Service. Paste the token after the yarn graph auth --product hosted-service command.
yarn graph auth --product hosted-service YOURTOKEN
Create configuration files for TypeScript and Git.
echo '{"extends": "@graphprotocol/graph-ts/types/tsconfig.base.json"}' > tsconfig.json
echo '.DS_Store\nnode_modules' > .gitignore
Smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain expose an application binary interface (or ABI) as an interface between client-side applications and the Ethereum blockchain. We will need this for our subgraph.
Download the contract’s ABI with cURL and save it to a file called Token.json.
curl "http://api.etherscan.io/api?module=contract&action=getabi&address=0xe7c29cba93ef8017c7824dd0f25923c38d08065c&format=raw" > Token.json
Create three project files including:
token.tsfor AssemblyScript code that translates Ethereum event data into the entities defined in the schemesubgraph.yamlfor a YAML configuration of the subgraph’s manifestschema.graphqlfor a GraphQL schema defining the data stored for the subgraph and how to query it via GraphQLecho > token.ts
echo > schema.graphql
echo > subgraph.yaml
Define Token and User entities
In schema.graphql we’ve defined two types, Token and User.
# schema.graphql
type Token @entity {}
type User @entity {}
The Token has a name and other information such as when it was created, the content URI, and the IPFS file path. It also includes information about the creator and owner.
# schema.graphql
type Token @entity {
id: ID!
tokenID: BigInt!
contentURI: String
tokenIPFSPath: String
name: String!
createdAtTimestamp: BigInt!
creator: User!
owner: User!
}
The creator and owner are User types. They have an id, an array of tokens they own, and an array of tokens they’ve created.
# schema.graphql
type User @entity {
id: ID!
tokens: [Token!]! @derivedFrom(field: "owner")
created: [Token!]! @derivedFrom(field: "creator")
}
@derivedFrom enables reverse lookups, which means we do not store both sides of the relationship to improve indexing and query performance. For one-to-many relationships, the relationship should be stored on the “one” side with the “many” side derived from it.
Create subgraph
The subgraph.yaml file will contain the definition of our subgraph. Start with the version of the specification used and a file path to the entity types in schema.graphql.
# subgraph.yaml specVersion: 0.0.4 schema: file: ./schema.graphql
Next is the network containing our data sources. dataSources.source needs the address and ABI of the smart contract.
# subgraph.yaml
dataSources:
- kind: ethereum
name: Token
network: mainnet
source:
address: "0x3B3ee1931Dc30C1957379FAc9aba94D1C48a5405"
abi: Token
startBlock: 11648721
dataSources.mapping.entities defines the entities that the data source writes to the store and is specified by the schema in schema.graphql.
# subgraph.yaml
mapping:
kind: ethereum/events
apiVersion: 0.0.5
language: wasm/assemblyscript
entities:
- Token
- User
dataSources.mapping.abis takes the name and file location of the ABI for the source contract.
# subgraph.yaml
abis:
- name: Token
file: ./Token.json
dataSources.mapping.eventHandlers lists the smart contract events the subgraph reacts to and the handlers in the mappings that transform these events into entities in the store.
# subgraph.yaml
eventHandlers:
- event: TokenIPFSPathUpdated(indexed uint256,indexed string,string)
handler: handleTokenIPFSPathUpdated
- event: Transfer(indexed address,indexed address,indexed uint256)
handler: handleTransfer
file: ./token.ts
Complete subgraph.yaml file:
# subgraph.yaml
specVersion: 0.0.4
schema:
file: ./schema.graphql
dataSources:
- kind: ethereum
name: Token
network: mainnet
source:
address: "0x3B3ee1931Dc30C1957379FAc9aba94D1C48a5405"
abi: Token
startBlock: 11648721
mapping:
kind: ethereum/events
apiVersion: 0.0.5
language: wasm/assemblyscript
entities:
- Token
- User
abis:
- name: Token
file: ./Token.json
eventHandlers:
- event: TokenIPFSPathUpdated(indexed uint256,indexed string,string)
handler: handleTokenIPFSPathUpdated
- event: Transfer(indexed address,indexed address,indexed uint256)
handler: handleTransfer
file: ./token.ts
Generate types
Generate AssemblyScript types for the ABI and the subgraph schema.
yarn graph codegen
Write mappings
Import the generated types and generated schema and create two functions: handleTransfer and handleTokenURIUpdated.
When a new token is created, transferred, or updated, an event is fired and the mappings save the data into the subgraph.
// token.ts
import {
TokenIPFSPathUpdated as TokenIPFSPathUpdatedEvent,
Transfer as TransferEvent,
Token as TokenContract,
} from "./generated/Token/Token"
import {
Token, User
} from './generated/schema'
export function handleTransfer(event: TransferEvent): void {}
export function handleTokenURIUpdated(event: TokenIPFSPathUpdatedEvent): void {}
handleTransfer loads the tokenId and sets the owner.
// token.ts
export function handleTransfer(event: TransferEvent): void {
let token = Token.load(event.params.tokenId.toString())
if (!token) {
token = new Token(event.params.tokenId.toString())
token.creator = event.params.to.toHexString()
token.tokenID = event.params.tokenId
let tokenContract = TokenContract.bind(event.address)
token.contentURI = tokenContract.tokenURI(event.params.tokenId)
token.tokenIPFSPath = tokenContract.getTokenIPFSPath(event.params.tokenId)
token.name = tokenContract.name()
token.createdAtTimestamp = event.block.timestamp
}
token.owner = event.params.to.toHexString()
token.save()
let user = User.load(event.params.to.toHexString())
if (!user) {
user = new User(event.params.to.toHexString())
user.save()
}
}
handleTokenURIUpdated updates the tokenIPFSPath anytime it changes.
// token.ts
export function handleTokenURIUpdated(event: TokenIPFSPathUpdatedEvent): void {
let token = Token.load(event.params.tokenId.toString())
if (!token) return
token.tokenIPFSPath = event.params.tokenIPFSPath
token.save()
}
Deploy subgraph
Build your project for deployment:
yarn graph build
Include your own GitHub username followed by the name of your subgraph:
yarn graph deploy --node https://api.thegraph.com/deploy/ USERNAME/logrocketgraph
The terminal will return a URL with an explorer for the subgraph and an API endpoint for sending queries.
Deployed to https://thegraph.com/explorer/subgraph/ajcwebdev/logrocketgraph Subgraph endpoints: Queries (HTTP): https://api.thegraph.com/subgraphs/name/ajcwebdev/logrocketgraph
You will need to wait for your subgraph to sync with the current state of the blockchain. Once the syncing is complete, run the following query to show the first two tokens ordered by id in descending order.
{
tokens(first: 2, orderBy: id, orderDirection: desc) {
id
tokenID
contentURI
tokenIPFSPath
}
}
This will output the following:
{
"data": {
"tokens": [
{
"id": "99999",
"tokenID": "99999",
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmdDdmRAw8zgmN9iE23oz14a55oHGWtqBrR1RbFcFq4Abn/metadata.json",
"tokenIPFSPath": "QmdDdmRAw8zgmN9iE23oz14a55oHGWtqBrR1RbFcFq4Abn/metadata.json"
},
{
"id": "99998",
"tokenID": "99998",
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmZwZ5ChjHNwAS5rFDGkom2GpZvTau6xzr8M7gro5HqQhB/metadata.json",
"tokenIPFSPath": "QmZwZ5ChjHNwAS5rFDGkom2GpZvTau6xzr8M7gro5HqQhB/metadata.json"
}
]
}
}
Query for the first user and their associated content:
{
users(first: 1, orderBy: id, orderDirection: desc) {
id
tokens {
contentURI
}
}
}
This will output the following:
{
"data": {
"users": [
{
"id": "0xfffff449f1a35eb0facca8d4659d8e15cf2f77ba",
"tokens": [
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmVkXqo2hmC2j18udhZG1KavxaTGrnEX7uuddEbghPKCUW/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmTSEgtJmptBCpEJKubK6xDZFiCMEHgGQjhrUAsJSXwzKZ/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmPzSJGhheyyA7MZMYz7VngnZWN8TinH75PTP7M1HAedti/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmeroC2cWfdN31hLd3JpBQMbbWqnQdUdGx94FGUR4AGBUP/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmQVkhqEsZvsstfDp6QAPXB4TkxFnpeAc9BWu2eQo6QvZD/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmRax3fw4skHp95i2v3BzroMoKQVHqAkwbov8FyPdesk3j/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmViGRnvHFBZ6CWHoxZGJoU9iwnoGwZfqj2vgDN3dgsGv4/metadata.json"
},
{
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmdRBPxDF1tUzm1Pczyme24vguUjW28cLwM4n9MvtxAWX6/metadata.json"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Query for the two most recently created NFTs.
{
tokens(
first: 2,
orderBy: createdAtTimestamp,
orderDirection: desc
) {
id
tokenID
contentURI
createdAtTimestamp
}
}
This will output the following:
{
"data": {
"tokens": [
{
"id": "133012",
"tokenID": "133012",
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmSmk85TjpaegCmHDRWZQqMz18vJtACZdugVx5a1tmfjpv/metadata.json",
"createdAtTimestamp": "1656792769"
},
{
"id": "133011",
"tokenID": "133011",
"contentURI": "https://ipfs.foundation.app/ipfs/QmU6RFcKFDteUTipg5tg4NFkWKApdVbo9oq9UYMtSmcWVe/metadata.json",
"createdAtTimestamp": "1653825764"
}
]
}
}
You can also use the HTTP endpoint and send GraphQL queries directly with cURL.
curl \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--url 'https://api.thegraph.com/subgraphs/name/ajcwebdev/logrocketgraph' \
--data '{"query":"{ tokens(first: 1) { contentURI tokenIPFSPath } }"}'
Conclusion
In this article we have seen how to create a GraphQL endpoint that exposes certain information contained on the Ethereum blockchain. By writing a schema containing our entities, we defined the information that will be indexed by the subgraph.
The quantity and diversity of blockchain networks continues to proliferate in Web3. Having a standardized and widely adopted query language will enable developers to iterate and and test their applications with greater velocity.
The post Web3 data querying with The Graph and subgraphs appeared first on LogRocket Blog.
from LogRocket Blog https://ift.tt/57ObrRJ
via Read more



