Tailwind and React are two leading technologies in their sphere. Tailwind CSS simplifies the concept of Atomic CSS, enabling developers to style their UI by adding some classes to their markup. And with the performance improvements that come with the new JIT compiler, Tailwind CSS has become a clear developer’s favorite.
Vite also simplifies the bundling process but takes a different approach than traditional bundlers. Vite gives us instant dev sever start times and ultra fast bundling by leveraging native JavaScript modules and esbuild under the hood.
Both Vite and Tailwind CSS excel in simplicity, performance, and developer experience.
As software becomes more sophisticated to meet the needs of end users, app size increases linearly and leads to a demand for faster development tools and bundlers. Although Create React App works well, as the app size increases, its performance declines. This is where Vite comes in.
In this article, we’ll learn about Vite and how to set up a React and Tailwind CSS application using it.
- Background information
- Vite vs. webpack and traditional bundlers
- Setting up a project with React, Vite, and Tailwind
Background information
Historically, JavaScript did not have an API for developers to write code in a modular way. This is because JavaScript was originally designed for small browser scripts.
Over the years, JavaScript has become wildly popular and is used in different aspects of programming. However, its main drawback has been its lack of modularity. This has led JavaScript developers to come up with different ways of creating modules, such as:
- IFFE modules, seen below:
(function () { // declare priate variables and/or functions return { // declare public variables and/or functions })(); - Third party module specifications such as CommonJS (CJS) and asynchronous module definition (AMD)
The problem is that not all module specifications work in the browser. For example, CJS supports only server-side module declaration. Additionally, building a modern web application involves the use of some libraries and packages that are not supported by the browser, like React, Vue, TypeScript, etc.
This problem, however, is solved by the concept of bundling. The process involves using a bundler (intuitive, right?) to combine all our app’s files and assets into a single package that works in the browser. This has led to the development of traditional bundlers such as webpack, Parcel, and Rollup.
There are two main issues with these: slow cold start of the dev server and slow updates. Next generation JavaScript build tools, like Vite, identify and solve these issues for us.
What is Vite?
Vite is the French word for fast. It’s is a modern build tool for frontend web development that leverages ES modules, or ESM. Vite features a leaner and faster bundler that comes with a preconfigured dev server.
Vite vs. webpack and traditional bundlers
As an ESM bundler, Vite solves the problems of traditional bundlers mentioned above. We’ll walk through a few key differentiators below.
Cold starting apps
Unlike webpack, Vite starts the dev server immediately when we cold start our application, as seen below:
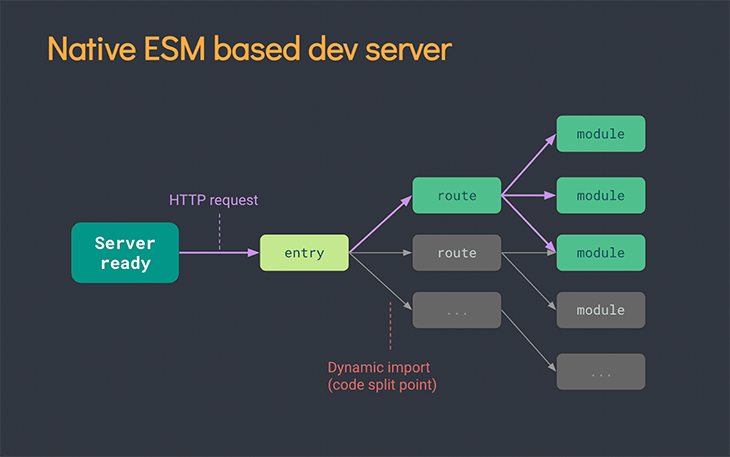
Vite can cold start the dev server instantly because of the following factors:
- Vite prebundles the app’s dependencies using esbuild, built with Golang, making it 10–100x faster than JavaScript bundlers. This redounds to the performance of Vite
- Vite dynamically determines which part of the code needs to be loaded by using route-based code splitting. Thus, Vite does not have to rebundle our entire application
- Vite only transforms and serves source code requested by the browser. This is possible because Vite serves our application code over native ESM, enabling the browser to take over some part of the bundling process in development
Bundling process
When compared to traditional bundlers like webpack, Vite takes a different approach in the implementation details of its bundling process. traditional bundlers like webpack rebuild the whole app on each update. The main problem with this is that it can get very expensive.
To address this issue, these bundlers use a technique called Hot Module Replacement, or HMR. HMR is a way of updating the changed modules in a running application so you don’t have to update the rest of the page.
However, the update speed of HMR decreases linearly as the app size grows.
Since Vite uses ESM, it performs HMR over ESM. This enables Vite to only invalidate the chain between the updated module and its closest HMR boundary when a module is updated. Thus, HMR in Vite is consistently fast regardless of the size of the application.
Performance advantages
Vite uses the browser to speed up full page reloads by leveraging HTTP headers. It handles cache dependency module requests via Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable, so they don’t hit the server again.
Lastly, source code module requests are made conditional via 304 Not Modified.
All these give Vite a significant performance advantage over bundle-based build tools.
Code splitting
Another major difference between Vite and traditional bundlers is the handling of code splitting. Traditional bundlers like webpack and Rollup produce common chunk — code that is shared between two or more other chunks. This, when combined with dynamic import, can lead to multiple network round trips as shown below:
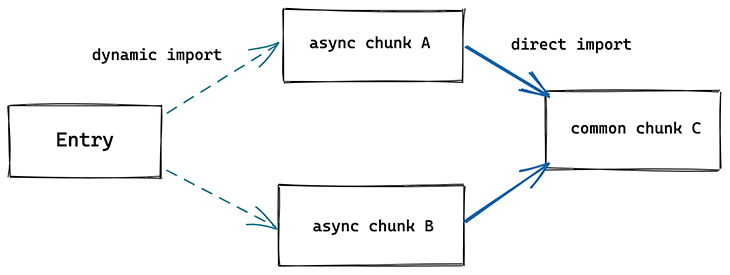
As shown in the image, in unoptimized scenarios when async chunk A is imported, the browser has no way of figuring out it needs common chunk C without first requesting and parsing A. And after it figures out it needs common chunk C, it then imports it, leading to an extra network round trip.
Vite implements the code split dynamic import calls in a different way that adds a preload step. This way, when chunk A is requested, chunk C is fetched in parallel. This completely eliminates network round trips.
When compared with Create React App, Vite outshines it in terms of performance for the reasons listed above. Although both are Node.js applications that can ultimately achieve the same thing, the one drawback with Create React App is its performance.
While Create React App works only for React, Vite is framework agnostic and supports a lot of libraries and frameworks out of the box.
In the next section, we’ll learn how to work with Vite by scaffolding a React application with Vite.
Setting up a project with React, Vite, and Tailwind
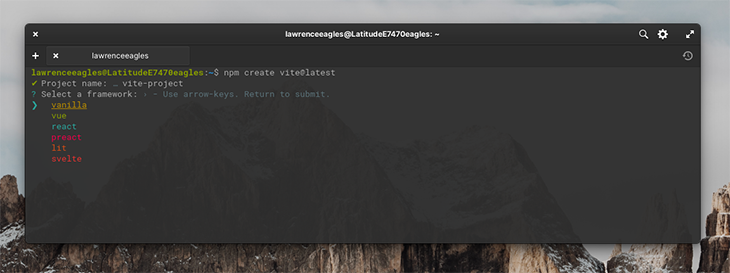
To scaffold a project, run the following code from your terminal:
npm create vite@latest
Choose a project name and select a template. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup, as seen below:
Alternatively, we can select a template by using the — template flag in the CLI, as seen in the code below:
# npm 6.x npm create vite@latest my-vue-app --template vue # npm 7+, extra double-dash is needed: npm create vite@latest my-vue-app -- --template vue # npm 6.x npm create vite@latest my-react-app --template react # npm 7+, extra double-dash is needed: npm create vite@latest my-react-app -- --template react
Next, install the app dependencies and start the dev server by running:
# Installs dev dependencies npm install #Starts dev server npm run dev
And we get:
Now we will integrate Tailwind CSS. The most seamless way to do this is to use postCSS by following the steps below:
First, install Tailwind CSS and its peer dependencies by running:
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
Next, create your tailwind.config.js file by running:
npx tailwindcss init
Add Tailwind to your postCSS configuration. To do this, create a postcss.config.js file and add the following code:
module.exports = {
plugins: {
tailwindcss: {},
autoprefixer: {},
}
}
Vite automatically applies all valid postCSS configuration in the postcss.config.js object to all imported CSS.
Configure your template paths by modifying the tailwind.config.js file as seen below:
module.exports = {
content:["./src/**/*.{js,jsx}"],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
}
Add the Tailwind directives to your CSS by replacing the code of your index.css file with the following code:
@tailwind base; @tailwind components; @tailwind utilities;
Now, run the build process by running npm run dev. You can see that Tailwind CSS styles have been applied.
To see this in action, we can apply some Tailwind CSS classes to the counter app.
In the src directory, create a components directory.
In the components directory, create a Counter.jsx component with the following code:
import React, { useState } from "react";
const Counter = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
<div className="flex h-screen">
<div className="m-auto">
<div className="text-6xl text-red-600">{count}</div>
<button className="px-6 py-2 rounded bg-green-800 hover:bg-green-600 text-white" type="button" onClick={() => setCount((count) => count + 1)}>
count+
</button>
</div>
</div>
)
}
export default Counter;
Now replace the App.jsx component with the following code:
import Counter from './components/Counter'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Counter />
</div>
)
}
export default App;
Now, we get:
And this confirms that we have successfully bootstrapped our application with Vite, React, and Tailwind CSS!
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about Vite and how it works. We compared Vite with traditional bundlers like webpack and saw that Vite has some clear performance advantages, as well as learned how to work with Vite by bootstrapping a React and Tailwind application.
By following this, I do hope you are ready to give Vite a try in your next React application.
The post Setting up a dev environment with React, Vite, and Tailwind appeared first on LogRocket Blog.
from LogRocket Blog https://ift.tt/Vubl6j8
via Read more



